Cats are beloved pets in many households. Their unique personalities and playful nature endear them to many owners. However, many people do not fully understand their senses and perception despite living with cats. In this article, we will learn the cat’s eye anatomy and vision to comprehend better what colors can cats see. We will explore their visual range and capabilities to get a glimpse into their world from their perspective.
Cat Vision: Understanding Cat Eye Anatomy
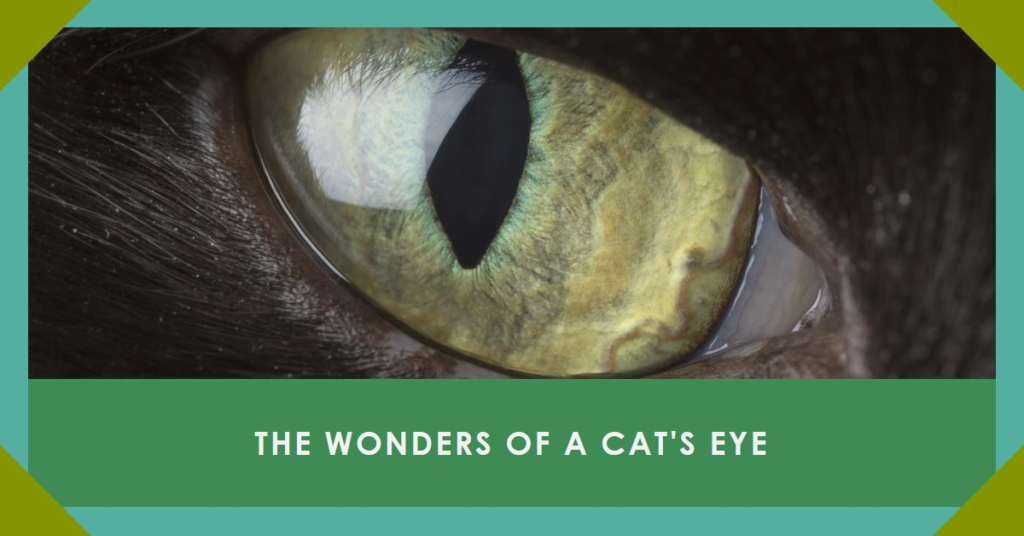
Cats have excellent vision that helps them thrive as hunters in the wild. Their eyes are adapted for low-light vision and detecting movement. A cat’s eyes are positioned on the front of its head, providing binocular vision and depth perception. This aids them in judging distances and catching prey.
The retina at the back of each eye contains two types of light receptor cells – rods and cones. Rods help with night vision and detecting movement, while cones allow color discrimination during the day. Cats have fewer cones than humans, limiting their ability to distinguish colors like ours.
Their retinas also have a reflecting layer called the tapetum lucidum, which enhances low-light vision. This is why a cat’s eyes can appear to glow in the dark when a light is shined on them. Their anatomy is tuned for nocturnal and crepuscular lifestyles as hunters.
What Colors Can Cats See?

Cats possess only two types of cones in their retinas compared to three in humans. This means they are essentially dichromatic or “color-blind,” like some forms of human color blindness. Research shows that cats can see blue and yellow/green light but are not sensitive to red light.
They cannot distinguish red and green, which appear to be the same color. Other colors like orange and purple also look similar. Cats can generally perceive wavelengths ranging from 400-700 nanometers, encompassing blue, purple, blue-green, cyan, yellow, and turquoise hues. Shades of red, orange, and all other colors along the spectrum appear muddy or darker to cats.
How far can cats see?
While cats may not see the full-color range, their vision is still very impressive. A cat’s visual activity or clarity of vision is about 20/100, meaning they can see at 20 feet what a human with normal vision can see at 100 feet.
Some studies indicate that their acuity may even be as good as 20/60, which is better than that. Cats can see great details from relatively far distances thanks to their big pupils and high photoreceptor density in the retinas. Their binocular vision and field of view also provide good peripheral vision for detecting movement. All these abilities make cats highly efficient hunters in nature.
Do cats have night vision?
As nocturnal predator ancestors, cats have remarkable night vision. Their eyes are five times more light-sensitive than human eyes. In very low light levels like moonlight, a cat’s night vision is up to six times better than a human’s. Cats can see in light, about one-sixth the level required for a human to see.
This is due to the high concentration of rod cells in their retinas and the reflective tapetum lucidum layer behind. These adaptations help cats hunt even in near-complete darkness. The tradeoff is that their vision is more sensitive to bright light than ours, so cats often have trouble with glare from direct light sources.
Do Cats See Color the Same Way as Dogs?
While cats and dogs have limited color vision compared to humans, some key differences exist in their abilities. Dogs have more cone receptor types than cats do – they can see blues and yellows clearly but also have some detection of reds and greens. However, research indicates canine vision may still appear more grayscale than colorful.
On the other hand, cats lack sensitivity for longer wavelengths almost entirely and see a more restricted range dominated by blues, purples, and luminance. So, in summary, dogs can distinguish a broader range of colors than cats, but color likely looks less vivid to both companion species than it does to humans.
Color Blindness in Cats
As discussed earlier, the limitation of only two cone types in cats makes them dichromatic or color-blind to certain colors. This is normal feline vision. However, like humans, some cat individuals can also have genetic color vision defects. A rare congenital condition called complete color blindness, where cats lack functioning cones, has been observed.
More commonly than full-color blindness, cats may suffer from “blue-yellow” color vision deficiency similar to some types of human color blindness. Such cats have problems distinguishing between blue, green, and yellow and various variations. Veterinary eye exams that use specialized tests can determine if a cat has hereditary color vision impairment.
Do All Cats See Color the Same?
Not all cats see colors exactly alike. Some have genetic eye conditions that make their vision different. Scientists found that some cats cannot see colors well or cannot see red at all. This is like people who are color-blind. Most cats just see fewer colors than people. But every cat’s eyes are unique and may see colors in their own way.
What Color Objects Do Cats React To?
Cats notice blue and green things. They chase toys or treats that are blue or green. Cats pay less attention to red things because red looks dark to them. Orange also looks more brown than bright. Cats see bright yellow and cyan best of all. When picking things for cats, brighter blues and greens are most interesting. Cats have less interest in dark colors like red, maroon, or forest green.
How Do Cat Toys Use Color?
Cat toy makers know what colors cats like. Many toys have feathers or light blue, green, or yellow strands. These pop out, so cats chase them. Some toys have these colors mixed with others, and cats see less. The colors cats see good get their attention. The other colors are there, too, but they don’t look as bright. This helps cats have fun playing!
Do Cats Learn To See More Colors?
As kittens, cats learn what colors mean. If their human often has red toys or food, cats may start to know red things are for play or eating. With time and experience, adult cats recognize more colors than basic blue and yellow. But cats will never see the whole color range like us. Their eyes can only see so much. But with enrichment, cats understand what different colors signify in their world.
Conclusion
While cats can perceive blues and yellow/greens thanks to their cone receptors, they are not sensitive to red wavelengths. Their color vision is confined to a narrower spectrum compared to humans. However, cats compensate for this with other excellent visual abilities like remarkable low-light sight, wide visual field, and high visual acuity.
Understanding a pet cat’s visual limitations and strengths provides insight into how they experience the world. It also helps owners ensure their curious feline friends can safely navigate their homes by day or night despite differences in what colors cats can see.
FAQs
1. Can cats see colors?
Yes, cats can see some colors, but not as many as humans. Their vision is less sensitive to differences in color compared to humans.
2. What colors can cats see?
Research shows that cats can see blue and green hues best. They can also see shades of yellow and some reds, but their ability to differentiate between colors is more limited than humans.
3. Can cats see red?
Cats have some ability to detect red colors, but their vision of red is not as clear as greens and blues. Deep reds may appear quite dark to cats, almost black.
4. Why can’t cats see all colors?
Unlike humans, cats don’t have receptors for all visible light wavelengths. They lack receptors for red and some other colors. So, their color vision range is narrower, helping them detect movement in low light conditions.
5. How many colors can cats distinguish?
On average, cats can distinguish greyscales and variations of blue, green, and some shades of yellow. But they cannot distinguish as many colors as humans, who can see millions of colors. Scientists believe cats may only be able to distinguish around 5-10 colors.
Also Read:
- Cocker Spaniel Feeding Guide : 2024 Best Picks for Furry Friend
- Best Food for Beagle Dogs: What You Need to Know in 2024


